The Gartner cyst is a cyst in the upper third of the vagina that is believed to be favored by retarded relics of the Gartner gang. The cysts are relatively large, but usually do not cause any discomfort. According to an incidental finding, the cyst is dissolved by puncture or surgery.
What is a Gartner Cyst?
Cysts are fluid-filled cavities that appear encapsulated and lined with epithelium. They can be found in almost all tissues and in a wide variety of parts of the body. One group of cysts are, for example, vaginal cysts that can appear in the vaginal wall. In addition to inclusion cysts, Gartner cysts are one of the most important sub-categories of vaginal cysts.
Gartner cysts are relatively large in shape and arise from remnants of embryonic tissue. Most Gartner cysts are located in the upper two thirds of the vagina and affect the tissue of the Gartner duct, the origin of which is the embryonic mesonephric duct or Wolff duct. The Gartner cyst affects between one and two percent of all women.
Age does not play a role in the development. The number of unreported cases is probably much higher. Since the cysts rarely cause discomfort, they are likely to go undetected many times. Gartner cysts without an epithelial lining are so-called pseudocysts and can therefore not be called true Gartner cysts.
Causes
The development of a cyst can be related to a number of different causes. Like those in the breast or the ovaries, the influence of hormones is also discussed as a causal factor for cysts in the vagina. Process disorders and parasites or hereditary connections are also under discussion. So far it has only been proven that Gartner cysts form from tissue remnants of the Gartner duct.
Since this passage corresponds to a relic from the mesonephric duct, disturbances during embryonic development can also play a role in a predisposition to Gartner cysts. In female embryonic sexual differentiation, the urnal duct gives way completely and leaves only small remnants. Gartner cysts appear to affect women who have retained an area in the lower portion of the urination duct.
The definitive causes of the vaginal cyst remain unclear. As with all other cysts, a wide variety of relationships and combined factors can be imagined. Both external and genetic factors can play a role.
Symptoms, ailments & signs
The vast majority of all vaginal cysts are completely asymptomatic. Since the Gartner cyst is a relatively large cyst, it may be possible for patients to feel it. Those affected usually describe the tactile findings as a plump and elastic bulge into the vaginal lumen. All other symptoms depend primarily on the exact size of the Gartner cyst.
If symptoms exist at all, the symptoms are in most cases absolutely unspecific symptoms. For example, a heavily bulging vaginal wall can interfere with sex life. Some patients describe pain during intercourse. Others are much more likely to have inflammation of the bladder. This phenomenon can be explained by the fact that, depending on their exact location, large Gartner cysts may accumulate bacteria.
These can be pushed into the urinary tract and the bladder and cause inflammation there. In most cases, however, patients do not see a doctor about symptoms that arose from the Gartner cyst. Often they are even disturbed by the findings because of the absolute asymptomatic nature of the phenomenon. Gartner cysts only burst in absolute individual cases before they are even noticed. In this case, severe pain and bleeding may occur.
Diagnosis
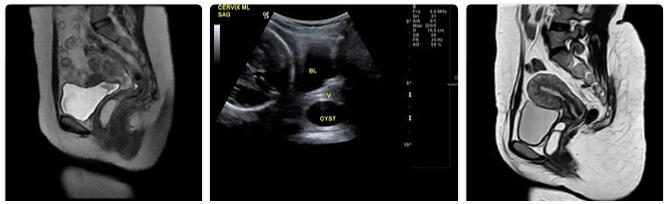
The Gartner cyst is in most cases an incidental gynecological finding. An MRI is used to confirm the suspected diagnosis of a vaginal cyst and to identify the cyst as a Gartner cyst. Gartner cysts have a high signal intensity in the context of T2-weighted image sequences of the MRI and show either a low or a medium intensity of the signal in T1-weighted sequences of the MRI.
In individual cases, the signal intensity depends on the protein content of the interior of the cyst. A cyst puncture clarifies the question of the benign nature of the anomalies discovered. The fluid from the cyst is given to the laboratory and examined histologically there. Gartner cysts are associated with a favorable prognosis and are not prone to degeneration.
Complications
In most cases, the Gartner cyst will not cause complications or discomfort. Most of the time, this is also not noticed, as there is no pain or other complaints. If necessary, the patient can feel the Gartner cyst and therefore have an examination carried out. The cyst is therefore often diagnosed at an early stage so that treatment can take place immediately.
In many cases, the strong bulge leads to pain during sexual intercourse. These can also negatively affect the other partner and lead to psychological complaints. In severe cases, the bladder can become inflamed, which is painful and, in the worst case, can lead to insufficiency. Typically, Gartner’s cyst is treated before it bursts.
Treatment only needs to take place if the cyst is malignant and therefore needs to be removed. The removal is usually without complications. In most cases, benign cysts are not removed and will go away on their own. Surgical interventions are also used for pain. The Gartner cyst does not reduce life expectancy.
When should you go to the doctor?
Since the Gartner cyst is often completely symptom-free for the patient, in most cases it is not detected until a routine examination. It is generally advisable to take part in the check-ups offered in order to be able to identify and treat diseases at an early stage.
If there are any symptoms beyond this, a doctor should also be consulted outside of the annual gynecological examination. If you feel generally unwell, have a vague feeling that something may be wrong, or if you have sexual disorders, a doctor is advisable.
If there is an unusual discharge from the vagina or if the habitual body odor of the genital area changes, the observations should be discussed with a doctor. A purulent discharge indicates conditions that need treatment. A doctor is needed in the event of irregular menstrual bleeding, pain during sexual intercourse or changes in libido.
A doctor’s visit is also necessary if irregularities are noticed through your own scans in the vaginal canal or on the cervix. If you experience bladder inflammation, general irritability, or unusual bleeding, see a doctor.
If there is pain or a feeling of pressure in the abdomen, it is also necessary to consult a doctor. In rare cases itching or an inner restlessness set in. The person concerned should bring this information to a doctor if it lasts for several weeks.
Treatment & Therapy
A benign and symptom-free Gartner cyst does not necessarily have to be treated. In many cases, cysts will resolve on their own. For this reason, it can make sense to wait, for example, before an intervention. Regular checks should at least take place during this time. If the cyst is causing discomfort, it should be removed without waiting.
Removing a Gartner cyst can be a minimally invasive procedure. For example, puncturing the cyst can drain the fluid it contains. The cyst then ideally regresses. If a relapse occurs and the encapsulation refills with fluid, a minor operation will be performed. Surgery is also the method of choice for painful Gartner cysts.
The cyst can be completely removed during the surgical procedure. This prevents it from filling up with liquid again after a long time. If the patient declines the operation despite a recurring Gartner cyst, she should at least attend regular check-ups. Although the risk of degeneration in Gartner cysts is rather low, degeneration cannot be completely ruled out.
Outlook & forecast
The prognosis for a Gartner cyst is generally favorable. The benign tissue changes often lead to no impairment and go unnoticed by the person concerned. Incidental findings lead to a diagnosis that does not always entail treatment. Since the Gartner cyst can grow in size, there is still the possibility of tightness or disturbances in sexual activities at any time.
Although the growth of the cyst can cause various symptoms, the prognosis for these cases does not change. It remains good. If the doctor and patient decide to remove the cyst, the usual complications can arise. Surgical intervention is generally associated with risks that can also occur with local anesthesia. After successful removal and healing of the wound, there is automatically no symptoms.
However, a Gartner cyst can develop again in the course of life. If the tissue changes develop again, the prognosis remains favorable.
In rare cases there is a malignant course of the disease. The cyst mutates and cancer cells spread throughout the body. This leads to a worsening of the prognosis. The sooner a diagnosis can be made and treatment initiated, the better the chances of recovery. Without medical care, there is a risk of premature death.
Prevention
Gartner cysts are likely to develop when large portions of the Garnter duct are left behind. Removing Gartner Gang relics may prevent Gartner cysts.
Aftercare
With a Gartner cyst, those affected have only very limited options for follow-up care. The patient relies primarily on the treatment and removal of this cyst to prevent further complications. In general, an early diagnosis with early treatment has a positive effect on the course of this disease and can prevent further symptoms.
The earlier the Gartner cyst is detected, the better the further course of this disease will usually be. In most cases, the Gartner cyst is removed by surgery. After such an operation, the person affected should always rest and take care of the body.
Here you should refrain from exertion or other stressful activities in order not to strain and strain the body unnecessarily. In many cases, additional follow-up examinations are required to ensure that the Gartner cyst has completely healed. Regular examinations after a successful procedure can also be useful.
Should the Gartner cyst lead to degeneration, the entire body must be examined for the occurrence of tumors. In most cases, this disease does not reduce the life expectancy of those affected.
You can do that yourself
A benign and symptom-free Gartner cyst does not necessarily need to be treated by a doctor. It is usually sufficient if the person concerned pays attention to adequate intimate hygiene and ensures that the cyst does not enlarge. However, if symptoms or serious complications arise, the gynecologist must be spoken to.
In addition to the medical treatment, various measures can then be taken, depending on the symptoms. If you have a bladder infection, warmth and lots of sleep help. Pain can be alleviated with medicinal herbs from nature, but also with warm compresses or a hot bath with essential additives.
At the same time, it must be decided together with the doctor whether the cyst should be removed. Surgical removal of the cyst is unproblematic and does not require any special preparation by the patient. However, it is advisable not to take any luxury foods before the procedure and otherwise follow the instructions of the responsible doctor.
After the operation, the affected person should take sick leave for a few days. Then bed rest and rest is indicated. In addition, the site of the operation should be carefully observed and examined by a gynecologist once a week, because this is the only way to rule out complications beyond any doubt.