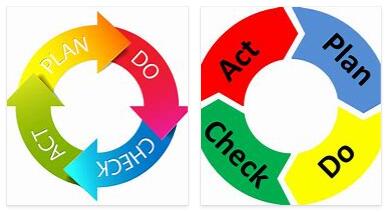
What is PDCA?
PDCA is also known to many under the terms Deming circle or Shewhart cycle . In quality management, PDCA represents an important basic concept in order to guarantee a constant improvement process. This applies both to the development of products and to the analysis of the causes of errors. PDCA is an abbreviation and stands for P lan- D o- C heck- Act. Translated, this means planning-executing-checking-adapting. It may sound a bit complicated, but you can easily apply it in your company and, above all, use it sensibly. The PDCA cycle represents a problem-solving process in four steps. PDCA is designed for long-term use and you are pursuing the goal of creating a good basis for quality management in your company.
Where does the PDCA come from?
Short for Plan, Do, Check, & Act by abbreviationfinder, PDCA is not a newfangled invention. Rather, the origins of this approach go back around 400 years. Ronald D. Moen and Clifford L. Norman were able to trace the origin of this method. They came across a combination of experiments by Galileo and Francis Bacon, who was known for his inductive learning. PDCA finally found its form through Shewhart and his student William Edward Deming. Deming took the findings from Shewhart and designed his form of the PDCA. This was presented by him in Japan in 1950. The Japanese took up this form and in turn developed the now known Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle from it.
Basics of the PDCA
As mentioned above, Walter Shewhart is counted as the father of this concept. He also laid the foundations. But Deming brought the insights of his teacher, who was a passionate analyst of data and quality improvements, into its present form. Deming turned the model into a real learning and improvement cycle. He did so for good reason. After the Second World War attempts were made to rebuild the economy in Japan. General Douglas MacArthur was in charge of this. But even he was unable to remedy the severe quality deficits. He therefore invited Deming to Japan as an expert in quality assurance. The most obvious difference between Shewhart’s and Deming’s PDCA fundamentals is that the latter added another level to his master’s process.
“Always touch a running system” instead of “Never touch”
And so the PDCA cycle came about, as it is known today and is also used. The PDCA method with its four phases .
The 4 phases of the PDCA
For a long time the Deming circle with its 4 phases was not correctly understood or incorrectly interpreted in the western economy. That may be a little bit due to the abstract nature of the circle and many entrepreneurs were of the opinion that we have been doing it ourselves for a long time. If you take a closer look at these 4 phases, however, that these are not improvements, as is generally assumed, but rather improvements. If you constantly only carry out improvements, then these only represent an intervention in an operative control loop. The aim here is only to correct certain and clear deviations. But with this you cannot achieve a long-term and above all sustainable improvement.
The PDCA cycle is a continuous process. He serves you as an entrepreneur to achieve the following points:
- Improving the quality of both products and processes
- Solution of problems
- Implementation of solutions
- Test of improvement measures on a small scale before the actual large implementation
To achieve this, the PDCA cycle is divided into 4 phases.
- plan
- do
- Check
- Act
Description of the 4 phases
| Phase | Description |
| plan | In order to set an improvement process in motion, it is necessary to plan and set goals in advance. In the first step, you therefore have to analyze the status quo . In your mind games, you should always consider questions about where there is potential for improvement and where the possible causes of problems are. |
| do | In the second phase you have the task of strategies which you have previously identified and procedures to implement . However, you have to note that these measures do not have to be implemented everywhere. First, you should do a test on a smaller scale. In this test you can then gather information on how the measures taken work. In this way, you can also deduce what to look for in the entire implementation throughout the company and what may have to be done differently. |
| check | When the test phase is over, an extensive analysis begins in addition to the control . But don’t make the mistake of seeing everything as positive. It is important that everything is viewed honestly and objectively. If you still find things that could jeopardize the achievement of your goals, you have to readjust now. Only then can you give your OK for the entire rollout. |
| act | The fourth step is the complete implementation and introduction in all areas of your company. The increase in quality that you have now achieved must be set by you as a standard. However, the work is not done with the completion of the improvement process. It is now important to monitor the continuous achievement of the goals set. After some time and good performance, you can start the next PDCA cycle if you discover further potential. |
What are the operational and evolutionary control loops
As already mentioned, the PDCA cycle with its four phases must be carefully considered. On superficial examination, you can quickly fall into the mistaken belief that everything is already being implemented and done with you. Therefore, you have to distinguish between the operational control loop and the evolutionary control loop .
The operational control loop
You always intervene in the operational control loop if errors or problems occur in the product, for example in the form of deviations. For such incidents, certain measures are already described in advance for the production process. These are then used in the event of deviations. In this way you can prevent many defective products or services from being produced. But all measures only serve this goal.
The evolutionary control loop
From the operational control loop, you can derive findings and results that not only make intervention in the production process necessary, but also need to be permanently remedied. These can be improvements in the conceptual design, improvement of processes or systems. These measures are then transferred back into the control loop later. With the evolutionary control loop, however, you can target and prevent deviations or other errors in the future.
PDCA in the field of quality management
In the area of quality management , PDCA plays an important role for every company. If you look at the evolutionary control loop, then you have to understand it as a never-ending process. There is neither a beginning nor an end. For this it is helpful if you imagine the Deming Circle as a spiral. A spiral that continues upwards. Every improvement takes your company to a new, better level. It is important that you do not look at everything from an individual point of view, but rather, as an entrepreneur, always think in both small and large PDCA cycles and act accordingly. For you, the following motto must always be in the foreground:
“Think every day anew whether there is anything you can do even better.”
It may sound simple now, but it isn’t quite. Because in order to be able to live this motto, you have to consider three essential factors .
- You have to see every single activity in your company as part of a process. And you can improve each of these individual parts.
- Fast and pragmatic solutions to problems, so-called quick hits, are fine, but they do not set the course for fundamental changes.
- You and your entire management team must act as role models when it comes to thinking and acting. If you only accept responsibility passively, this will not be enough in the long term.