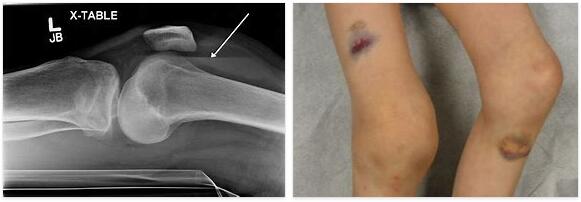
Hemarthrosis is the medical term for a bruise in the knee. A knee injury causes blood to accumulate in the joint.
What is hemarthrosis?
If the bruise is only minor, those affected only suffer from pressure pain and slight swelling. A typical feature of hemarthrosis is a bluish discoloration of the knee.
According to abbreviationfinder, the term hemarthrosis refers to a bruise in the knee. The term is to be distinguished from the term hematoma, which is a collection of blood anywhere in the body. A bruise is the leakage of blood from a broken blood vessel.
The blood then settles in a body cavity or tissue. The bruise becomes visible as a bruise that forms on the knee in the event of a hemarthrosis. The blood can no longer be transported away from the veins. Therefore, the knee fills with blood, leading to its thickening. In the further course, the bruise takes on a yellowish color and then disappears again.
Causes
Hemarthrosis can arise from a variety of causes. In most cases, the bruise in the knee is caused by injuries to the joint structures. Sometimes there are also long-term consequences due to wear and tear, chronic improper stress or sports injuries.
Some sports are considered particularly risky for the development of hemarthrosis. These primarily include football and skiing. The same applies to other sports in which knees and legs are exposed to heavy loads. There is also an increased risk of rotational trauma with the knee. If the lower leg twists too much towards the thigh, there is a risk of injury to the menisci, the collateral ligaments or the cruciate ligaments.
The range of injuries extends from ligament stretching to ligament tears. The sudden injuries often also affect the blood vessels that run through the knee. This, in turn, causes bruising to adjacent tissue and knee cavities.
It is not uncommon for hemarthrosis to be caused by external influences involving the kneecap (patella) or the bones. This is mostly due to serious falls. Hemarthrosis can be caused by a slight bruise or a bone fracture.
Sometimes surgical interventions on the knee are also responsible for the formation of a hemarthrosis. The body classifies the operation as an injury. Even taking certain medicines can cause hemarthrosis. If this is the case, the attending physician must prescribe another drug. It is not always possible to find a concrete cause for a bruise in the knee. This is how the hemarthrosis shows up without a previous injury.
Symptoms, Ailments & Signs
The symptoms of hemarthrosis depend on the extent of the bruising. If the bruise is only minor, those affected only suffer from pressure pain and slight swelling. A typical feature of hemarthrosis is a bluish discoloration of the knee. Initially, the injured area takes on a reddish discoloration, which later turns blue and yellow.
If the hemarthrosis is extensive, this is often noticeable through permanent and severe pain. Doctors also speak of tension pain. It occurs due to the swelling caused by the bruise spreading. In addition, the movement of the knee is restricted.
Diagnosis & course of disease
If a hemarthrosis occurs in the knee, a medical evaluation is recommended. There is a risk of further injuries to the joint or bones and severe pain. The doctor asks the patient to describe the course of the injury. This is often enough to make the right diagnosis.
If the hemarthrosis is in a deeper location, sonography (ultrasound examination) may be necessary. The course of a hemarthrosis depends on how quickly therapy is started. The lesions can usually be kept small with early treatment. Without rapid therapy, there is a risk of permanent movement restrictions and damage to the cartilage.
Complications
The symptoms and complications of hemarthrosis depend heavily on the severity of the bruise and its cause, with most cases being an accident. Swelling usually occurs and the affected person suffers from pain. The pain usually occurs in the form of pressure pain, but it can also occur as pain at rest, leading to difficulty sleeping.
The affected area turns red or blue and may also pulsate. If the hemarthrosis is not treated, the pain usually does not go away on its own and leads to a reduction in the patient’s quality of life. Furthermore, there are also limitations in movement, which can often lead to psychological problems. The everyday life of those affected is made more difficult and carrying out normal activities is no longer easily possible.
In most cases no direct treatment of the hemarthrosis is necessary and it goes away on its own. If the accident was serious, it may be necessary to have a doctor examine you. However, there are no particular complications or serious symptoms. Life expectancy is also not affected by hemarthrosis.
When should you go to the doctor?
Hemarthrosis is usually harmless and will go away on its own after a few days. Medical advice is needed if the bruise persists for more than a week. If there is severe pain or other symptoms, the hemarthrosis must be examined in any case. The bruise may be squeezing a nerve or pressing on surrounding tissue. Larger effusions can also cause severe tension pain and restricted mobility, which require the use of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Furthermore, you should go to the doctor with a hemarthrosis if there are other injuries or if a bruise has already occurred repeatedly. If the hemarthrosis occurs after knee surgery, the doctor in charge must be informed. Patients with chronic joint diseases or long-term sports injuries should also speak to the doctor and have the symptoms clarified. Other contacts are the orthopaedist, a sports doctor or a specialist in joint diseases. If the symptoms are severe, a visit to the hospital is indicated.
Treatment & Therapy
In most people, hemarthrosis resolves on its own, taking only a few days. The leaked blood coagulates and the organism breaks it down again with the help of enzymes. Due to the different degradation products, the discolouration changes to red, blue and yellow.
In order to counteract swelling of the knee, the patient should cool the joint immediately after the accident. In this way, the blood vessels constrict and the bleeding decreases or even stops completely. Since the bruise in the knee cannot spread any further, the swelling also decreases.
The doctor decides on further therapy. If the cause of the hemarthrosis is corrected, no further treatment is usually required. In this way, the bruise in the knee disappears completely after two to three weeks. To treat the pain, a special hematoma tape can be applied to the knee, which speeds up the healing process.
Sometimes, however, it is also possible that the hemarthrosis cannot heal on its own. In such cases, a joint puncture is performed. The doctor pricks the joint with a thin needle and sucks out the blood. The patient usually feels an immediate improvement. Arthroscopy (knee joint reflection) can also be performed.
Prevention
To avoid hemarthrosis, exercise caution. The knee should be protected from falls with special pads.
Aftercare
Follow-up care aims to prevent symptoms from recurring. This is well known from cancer diseases. Scheduled follow-up examinations should detect a tumor in the early stages and thus enable the best possible treatment. Aftercare for hemarthrosis, on the other hand, consists of preventive measures.
This is to avoid the causes of the disease. In concrete terms, this means that overexertion should be avoided during sporting activities such as soccer and skiing. The doctor treating you will inform you about the dangers as part of the initial diagnosis. However, the implementation of the behavioral recommendations is the responsibility of the patient.
If the progression is unfavorable, hemarthrosis can lead to long-term treatment. This is due to permanent damage. The typical complaints then include restricted movement and pain. Physiotherapy is then part of the medical assistance offered. Scheduled follow-up examinations that document the progress of the disease are agreed individually.
Their rhythm depends on the complaint situation. Sonography can be used to determine this. A hemarthrosis can also be visualized in deep places. Furthermore, the presented symptoms of the patient allow a diagnosis. In any case, aftercare aims to prevent the transition to arthrosis. This complication can cause further instability.
You can do that yourself
After an accident, the affected knee must first be cooled and immobilized. With the help of so-called hematoma tapes, which are glued to the affected skin, the swelling around the bruise can be further reduced. If the pain subsides quickly, the knee joint must be carefully observed for a few hours. If severe pain occurs or movement restrictions and other complaints occur, medical treatment is required.
Depending on which injury is diagnosed, various self-help measures can then be taken. Stretched ligaments and torn ligaments require medical therapy. The affected person cannot do much here, apart from taking care of the knee and making use of the routine examinations in the doctor’s office. Bruises usually heal on their own after medical treatment. It is enough to cool the hemarthrosis and, if possible, not to put any strain on the affected knee. Quark packs and other home remedies can sometimes accelerate the healing process.
An operation-related hemarthrosis must be presented to the doctor responsible immediately. After an operation, the knee should be closely monitored to avoid renewed bruising and the associated further complications.