An acid is a substance that, in solution, causes an increase in the concentration of hydrogen ions. Acids can be combined with bases for salt development. Fatty, meanwhile, is that which has fat (sebum, lubricant).
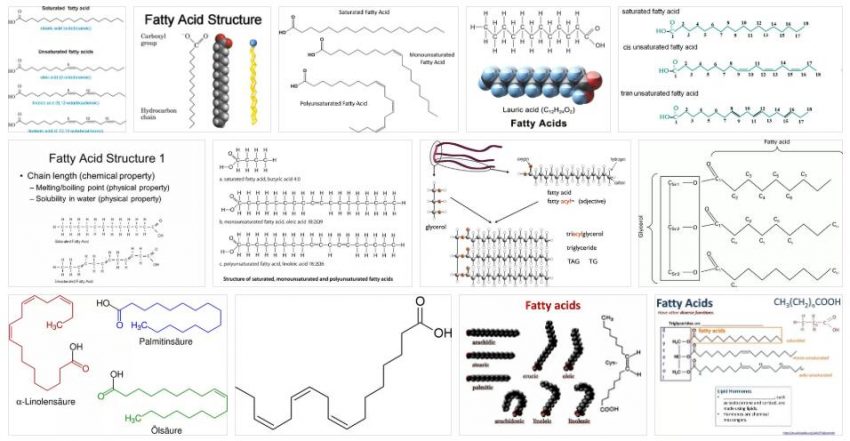
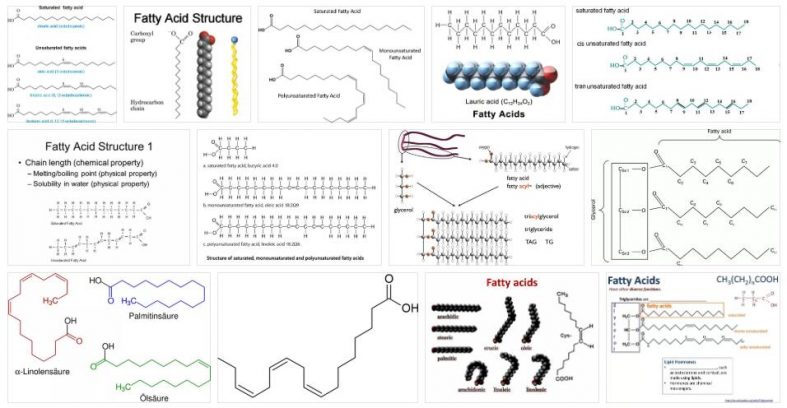
The fatty acids are biomolecules lipid constitution is formed from a linear hydrocarbon chain and extensive, with a carboxyl group at its end. As you can see, it is necessary to know the meaning of various concepts to understand what fatty acids are.
These acids are biomolecules: that is, molecules that make up living things. The lipids, moreover, are those molecules which are composed primarily of hydrogen and carbon. As for the carboxyl groups, they are sets of compounds that have a functional group of the carboxy or carboxyl type (they have a hydroxyl and carbonyl group on the same carbon).
The carbon atoms of fatty acids are linked through covalent bonds, either double or single. At one end of the chain, there is an atom with three free bonds that occupy the hydrogen atoms, while the rest of the atoms have two free bonds (occupied by other hydrogen atoms). At the other extreme, the carboxyl group appears, which combines with one of the hydroxyl groups to generate a reaction.
The lipid bilayer of the plasma membranes of cells is formed with these fatty acids, which belong to the groups of molecules known as glycolipids and phospholipids. In mammalian animals (including man), fatty acids are usually found as triglycerides, which are deposited in adipose tissue.
It is important to know, in addition to all the above, that fatty acids, if we take into account what their structure is at a chemical level, can be divided into three main groups:
-Maturaunsaturated, most of which are derived from nuts, salmon, vegetable oils such as wheat…
-The saturated, which are fats. We can say that they can be found in foods that are mainly of animal origin, such as, for example, butter, cheese, meat…
-Polyunsaturates, which are divided, in turn, into two groups: fatty acids omega 3 and omega 6 fatty acids.
In recent times, where there has been a notable increase in the number of people who are committed to taking care of their diet, we come across the fact that foods that provide omega 3 fatty acids have gained great prominence. Why? Because they are considered to bring numerous benefits to the body.
Specifically, it is ruled that they favor both the proper functioning of the brain and the nervous system, without forgetting of course that they do the same with the immune system. That without overlooking that they significantly improve blood pressure or coagulation, among others.
Omega 6 fatty acids, on the other hand, must be ingested in an absolutely moderate way and under control. Yes, because an excess in the body of them gives rise to serious health problems such as arteriosclerosis or even difficulties of an inflammatory nature.