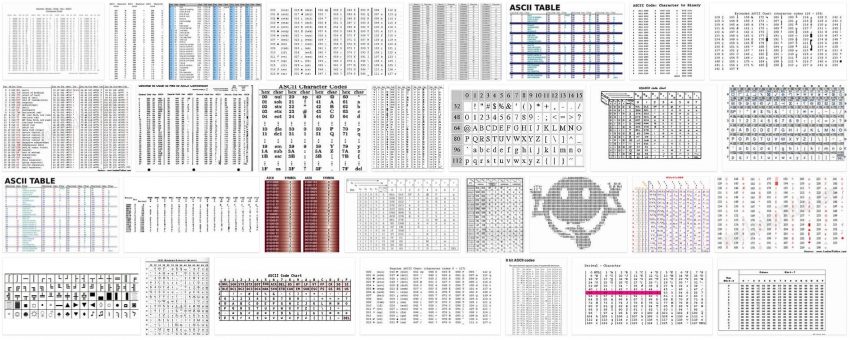
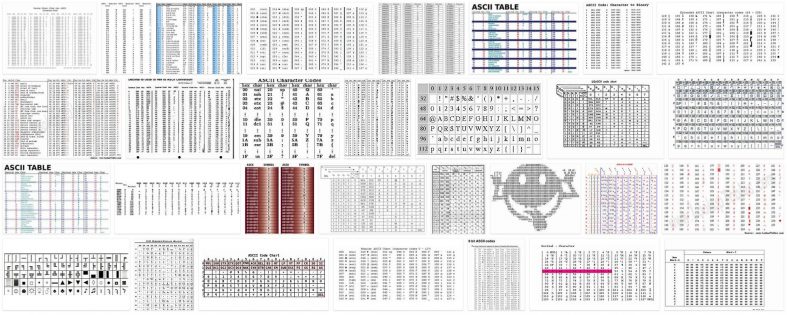
The ASCII code is an alphanumeric coding table of the Latin alphabet so that computer systems can store texts.
The name of the ASCII code comes from the acronym in English American Standard Code for Information Interchange , which is translated into Spanish as: American (American) standard code for information exchange.
The ascii code is ordered in a table where each number or combination of numbers corresponds to an upper or lower case letter, numbers and punctuation symbols adapted to the English language.
In computer science, the importance of the ASCII code is that it allowed computers to store texts, since computer systems are only capable of storing numbers. With the character coding system, the systems could translate the numbers into a letter or symbol and then store them in memory.
The first ascii code corresponded to a 7-bit code that generates 128 characters, since the computers work with a binary system. Over time the table and bits were expanding but did not cover characters from other languages such as Spanish, for example.
Due to the limitation of the ASCII code, today codes such as Latin-1 (ISO-8859-1), UTF-8 and UTF-16 are used for web pages and document.